Tetrahydrocannabinol or delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is one of the few cannabinoids that needs no special introduction, especially to people who understand cannabis and its numerous applications for medical and recreational purposes. The mind-altering activity of the compound makes it one of the most popular cannabinoids on the market.
The role of THC in the cannabis industry cannot be overemphasized, as it has played a key role in choosing strains and is a major factor in determining the safety and legal status of products.
Unlike THC, THCa doesn’t get you high. Although THCa turns into THC, It is one of the less researched cannabinoids, thanks to its limited concentration in the cannabis plant. The fact that it is a major component of raw cannabis products and easily gets converted to THC makes it harder to study. It is also pertinent to note that it is quite impossible to get high from consuming THCa and/or raw cannabis.
Why you can’t get high from raw cannabis
The raw cannabis plant is a storehouse of nutrients. It is often considered a superfood since it has a high nutritional value. The flowers, seeds, and leaves of the cannabis plant are rich in several nutrients that can play therapeutic and nutritional roles. The raw cannabis plant is also rich in inactive or what we call acidic cannabinoids, explaining why it is almost impossible to get high from eating raw cannabis.
The seed, flower, and leaves of the cannabis plant contain varying concentrations of the following nutrients/ compounds.
- Proteins
- Healthy fatty acids like omega 6 and omega 3
- carbohydrates
- Minerals like zinc, folate, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium, and iron
- Vitamins like Vitamin C, E, K, and trace B1, B3, and B6 amounts
- Cannabinoid acids
- Flavonoids
- Terpenes
- Fiber
A quick look at this list, and you can appreciate the benefits of raw cannabis juicing or adding it to your morning smoothie.
The Big Picture: Neutral vs. Acidic Cannabinoids
These cannabinoid acids so prevalent in raw cannabis represent the inactive forms of the compound and are very important in creating the neutral/active form such as THC or CBD.
Essentially, these cannabinoid acids start as cannabigerol acid (CBGa) and are further converted to tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa), cannabidiolic acid (CBDa), cannabichromenic acid (CBC), and more. These acidic cannabinoids are later converted to their neutral forms, THC, CBD, CBC, and CBC.
Although regarded as inactive cannabinoids, there are quite a few research studies that support the possible therapeutic potentials of cannabinoid acids.
For instance, a 2022 study shows the possible antiviral properties of CBGa, THCa, and CBDa in preventing the attachment of Covid-19 viral particles to host cells.
Cannabinoid acids may possess a better therapeutic activity than their neutral counterparts. For example, CBGa was found to be a better antioxidant agent than CBG. Another study in 2021 reported how acidic cannabinoid (CBGa) provided a better anticonvulsant activity than CBG. These and many more therapeutic activities are responsible for the increased interest in cannabinoid acids.
When comparing THC to THCa, they share some similarities and differences. Although they originate from the same plant, they exhibit different levels of interaction with the body, thus suggesting a unique therapeutic potential for each. Let’s dive into their world.
What is THC?
THC is one of the most abundant cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. It constitutes a large percentage of phytocannabinoids (depending on the strain) and is responsible for the psychoactive effect of cannabis. Note that delta-9 THC is one out of the 11 members of the THC-type cannabinoids.
The other compounds that may share a structural similarity with THC include;
- Delta-8-THC
- Delta 10-THC
- Delta-11- THC
Variants of the THC-type phytocannabinoid exhibit varying levels of psychoactivity.
While these compounds originate from different THCa molecules usually designated with the appropriate numbers, e.g., delta-9 THCa, delta-8-THCa, THC is a general term referring to delta-9 THC since it is the first THC to be synthesized in the plant.
Therapeutic benefits of THC
Thanks to its psychoactive nature, THC is one of the most researched cannabinoids. Although it can interact with different parts of the body, it has a higher affinity for receptors that are mostly expressed in the central nervous system (these are called the CB1 receptors).
The receptors play a critical role in controlling mood, pain, and other feelings, thus explaining why THC can produce euphoric feelings. Some of the therapeutic benefits of THC are listed below:
- Anticonvulsant
- Antiemetic
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anxiolytic
- Appetite stimulating
- Immunomodulatory
- Anticancer
- Muscle relaxant
- Neuroprotective antioxidant
- Psychotropic
- Reduce Intraocular pressure
- Slows Gastrointestinal motility
Possible side effects of THC
THC's most visible psychological effects have been divided into four groups; affective, sensory, somatic, and cognitive. The CB1 receptor mediates THC's most documented side effects since they are present in the central nervous system. Some of the possible side effects of THC are listed below:
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Decreased blood pressure
- Disinhibition
- Distorted perception
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Affects memory
- Hallucinations
- Impaired judgment
- Increased appetite
- Increased heart rate
- Learning Difficulty in thinking and problem-solving
- Paranoia
- Reduced coordination
- Sedation
Cannabis strains with high THC
- Grease Monkey
- Bruce Banner
- Ghost Train Haze
- Strawberry Banana
- 99 problems
- Weeding cake
- Ghost OG
- L’Orange
- Ultra Sour
- Tropicana
What is THCa?
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa) is one of the major constituents of fresh and undried cannabis. It is the inactive or neutral form of THC. It is the precursor cell for the creation of THC, CBN, and other variants of tetrahydrocannabinol like delta-8, delta-10, and delta-11 THC. It is naturally present in the cannabis plant and is synthesized from CBGa (the mother cannabinoid) via enzymatic activity. THCa is further decarboxylated into THC in the presence of heat. By exposing THCa to oxidation, it gets converted to CBNa and delta-8-THCa.
As one of the major constituents of raw cannabis, THCa is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid whose benefits are absorbed by the body via the raw consumption of flowers such as cannabis juicing. It is unstable and converts to THC or other psychoactive cannabinoids in the presence of heat or light.
Therapeutic Benefits
THCa is not only good for creating other cannabinoids. Research shows a varying degree of therapeutic activities. Some of these activities may be triggered by its interaction with several cannabinoid receptors.
These receptors regulate energy production, lipid metabolism, and inflammation. This supports the use of THCa as a neuroprotectant in Gliosis and Huntington's disease, for example. THCa also exhibits a weak affinity on CB1 receptors with no activity on CB2.
The other therapeutic benefits of THCa are listed below;
- Anti-inflammatory agent
- Appetite stimulant
- Sleep-related disorders
- Antispasmodic
- Anti-tumor
- Anti-COVID agent. THCa exhibits the second most potent binding affinity to COVID cells, thus preventing their attachment to host cells. Note that this was observed in-vitro and more research would be needed.
- Reduce obesity
- Immunomodulatory effect
Possible side effects of THCa
THCa is non-psychoactive. While this is not as widely researched as THC and other neutral cannabinoids due to its limited availability and unstable nature, some people believe it may share a similar side effect with THC. There is a likelihood of developing sensitivity to THCa if you are sensitive to THC. On this note, some of the possible side effects that may arise from THCa include:
- Increased heart rate
- Dry mouth
- Red eyes
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
Also, note that this may show up on drug tests, especially if you consumed the cannabinoid a few days before the drug test. THCa may also interact with prescription medications processed by the CYP450 (similar to how grapefruit interacts with certain meds).
Cannabis Strains with high THCa
- Amnesia Haze
- Blue Dream
- Bruce Banner
- Death Star
- Ghost Train Haze
- Gorilla Glue
- Laughing Buddha
- Lemon Kush
- Lemon
- Silver Haze
- Sour Diesel
- Thai
- The White
- White Tahoe Cookies
Check out cannabis strain reviews from The Bluntness here.
THC vs. THCa: Difference Between The Two
Psychoactivity
THC is a psychoactive cannabinoid that can trigger many psychotropic activities. This is due to interaction with CB1 receptors. Note that CB1 receptors are expressed in the basal ganglia, cerebellum, and cortex. These brain parts coordinate movement, pleasure, memory, and thinking. THCa is non-psychoactive and may provide a safer interaction and therapeutic activity.
Legal status
THC is considered illegal in several world regions, with acceptable limits of less than 0.3%. These regulations are silent on THCa. While THCa has not been classified as a controlled substance on the federal level possessing it could land you in trouble if you decarb cannabis.
Receptors involved
The therapeutic activity of cannabinoids depends on their interaction with receptors. While THC strongly interacts with CB receptors, THCa prefers to bind with PPaRγ receptors.
Stability
THCa is highly unstable since exposure to heat or light can convert it to THC, delta-8 THC, or CBN. This is why it is quite impossible to obtain the cannabinoid. However, certain cannabis strains are rich in THCa.
Need a little more Bluntness in your life? Subscribe for our newsletter to stay in the loop.









 Best Weed Smoking Games to Try - Jammin'
Best Weed Smoking Games to Try - Jammin' The 31 Best Weed Smoking Games To Try
The 31 Best Weed Smoking Games To Try The Best Weed Smoking Games
The Best Weed Smoking Games The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
 Stoner Games - Games to Play While High
Stoner Games - Games to Play While High The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
 The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
 The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play The Best Weed Games to Play
The Best Weed Games to Play The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try Games for Stoners
Games for Stoners  woman in white and blue floral shirt sitting beside woman in white and black floral shirtPhoto by
woman in white and blue floral shirt sitting beside woman in white and black floral shirtPhoto by 
 The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Play
 The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try world map with pinsPhoto by
world map with pinsPhoto by 
 The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try
The Best Weed Smoking Games to Try






 Recognizing the Signs of Antisocial Behaviors - The Bluntness
Photo by
Recognizing the Signs of Antisocial Behaviors - The Bluntness
Photo by  Weed Makes Me Antisocial: What To Do - The Bluntness
Photo by
Weed Makes Me Antisocial: What To Do - The Bluntness
Photo by 
 Ayrloom Orchard Sunrise Cannabis Infused Gummies
Ayrloom Orchard Sunrise Cannabis Infused Gummies Ayrloom Island Time THC Gummies - Pineapple Mango Flavor
Ayrloom Island Time THC Gummies - Pineapple Mango Flavor Ayrloom Pillow Talk - Sleep Gummies
Ayrloom Pillow Talk - Sleep Gummies 
 The Truth About THC Candle: Cannabis Candles & How to Make Your Own - The Bluntness
Photo by
The Truth About THC Candle: Cannabis Candles & How to Make Your Own - The Bluntness
Photo by 
 Humankind has been using THC for millennia.
Humankind has been using THC for millennia.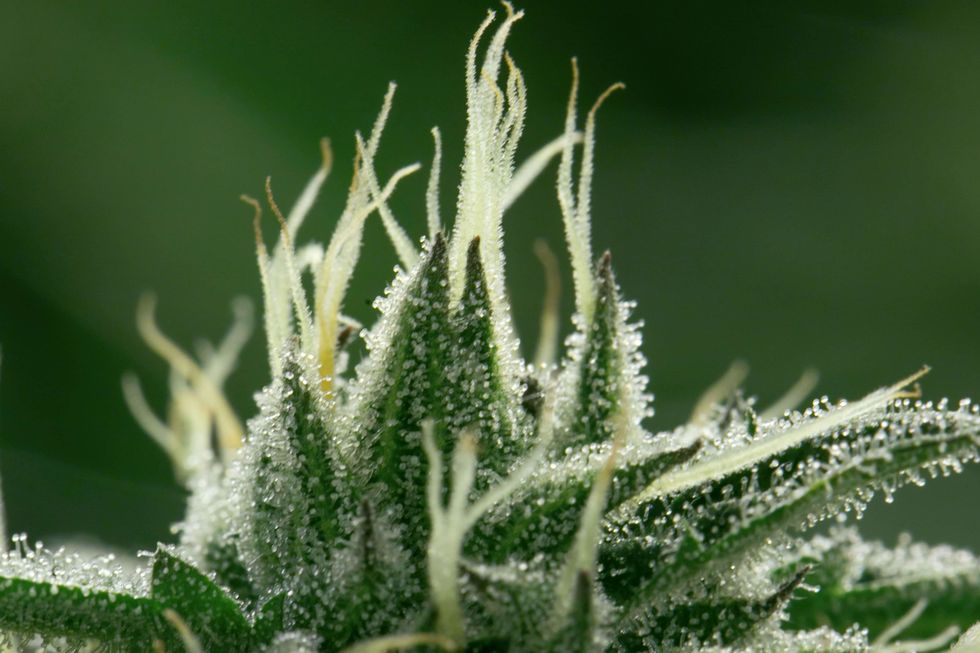 Those little, sugar-like crystals are the sticky trichomes that house special chemicals including cannabinoids and terpenes.
Those little, sugar-like crystals are the sticky trichomes that house special chemicals including cannabinoids and terpenes. Raw cannabis typically contains very little THC. Instead you get non-psychoactive THCA, which is converted into THC.
Raw cannabis typically contains very little THC. Instead you get non-psychoactive THCA, which is converted into THC. Cultivators are now breeding cannabis not just for THC, but other cannabinoids such as CBD, THCV, and more.
Cultivators are now breeding cannabis not just for THC, but other cannabinoids such as CBD, THCV, and more. Getting the most out of cannabis usually requires a bit of guidance and patience.
Getting the most out of cannabis usually requires a bit of guidance and patience. A lot of people think CBD is medical, and THC is for fun. This is an unfortunate misconception.
A lot of people think CBD is medical, and THC is for fun. This is an unfortunate misconception. THC has a surprising amount of medical benefits.
THC has a surprising amount of medical benefits. For some the cannabis high is an unwanted side effect, for others it's the main show.
For some the cannabis high is an unwanted side effect, for others it's the main show.